Assessing the Water-Land-Energy-Food Nexus in trans-boundary river basins
|
Status: ongoing
Partner: UNECE |
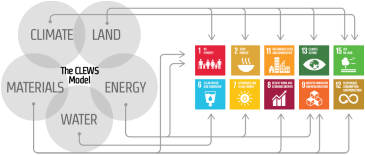
Typically water management schemes and ecosystem preservation plans differ from one riparian country to another as well as between scales. Bilateral or multilateral agreements on water management are becoming urgent as pressure on natural resources increases. Often a lack of integration between sectors and country policies causes significant efficiency losses. Considering the water, energy, land-use and ecosystems nexus in trans-boundary basins aims at identifying these linkages and understanding how best to integrate them in future planning, to improve the efficiency of resources use while preserving the ecosystems and their services... more
image source: unece.org |
Country level CLEWs
Development of the Model Management Infrastructure (MoManI) interface.
|
Status: ongoing
Partner: UNDESA |
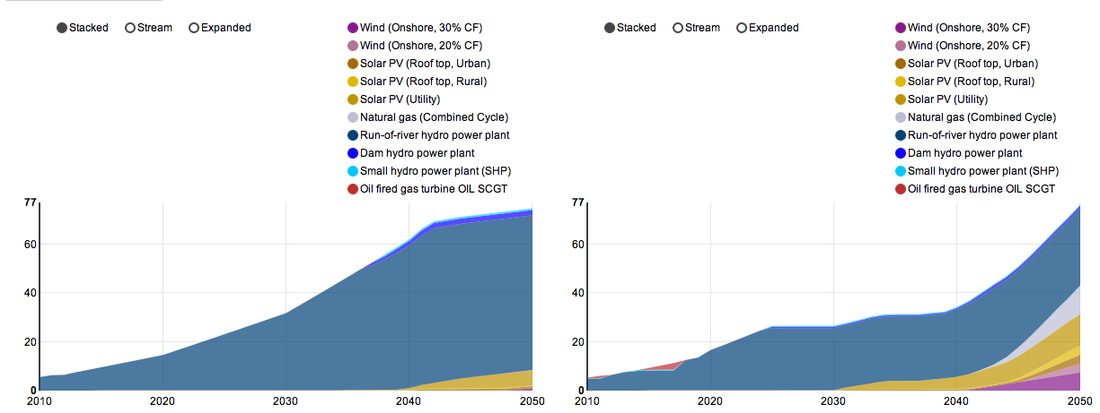
To facilitate the use of OSEMOSYS for capacity building and model-based planning, UNDESA and KTH-dESA (with support from IAEA and Tartu University) are developing the web based interface Model Management Infrastructure (MoManI). MoManI, is a browser-based open source interface for energy systems modelling. Available to all manner of users, from policy makers and energy planners through to academics, its novel structure allows different teams to collaborate simultaneously from around the globe. Each user can easily edit and update any part of the modelling process: from the underlying mathematical equations of OSeMOSYS through to the visualization of results. Although energy system modelling is a complex process, MoManI’s straightforward structure helps simplify it thereby supporting effective capacity building activities. The easy and fast results visualization feature in MoManI also allows energy planners to get immediate feedback on their work to ensure a quick turnaround time.
Link to the project: https://unite.un.org/sites/unite.un.org/files/app-desa-atlantis/index.html Link to MoManI: osemosys.momaniweb.com |
Energy systems-CGE modelling Link up for pilot countries
|
Status: ongoing
Partner: UNDESA |
The project aims to support the development of government capacities to formulate consistent policies and strategies aimed at promoting sustainable development. Sustainable development requires the alignment of a wide range of policies in a coherent framework, to ensure that decisions aimed at achieving human development and poverty reduction in a context of intensive use of renewable energy sources and protecting natural heritage, are made so that macroeconomic balances are preserved and to ensure the sustainability of public finances. Therefore, the project will train and will provide the government with a suite of tools that includes a comprehensive model of the economy, a dynamic model of power systems, a routine microsimulation and a methodology link between models of economy and energy . The comprehensive model of the economy (a CGE model with focus on energy) is being developed by UNDESA and the energy systems model is developed in OSeMOSYS by KTH. The project includes several training activities which aim to deepen the participants' ability to build energy system and CGE models from scratch and also develope capacities for interpretation and communication of results. The pilot countries were Uganda, Nicaragua and Bolivia.
|
SweGRIDS
Climate Vulnarability of the African Infrastructure
|
Status: completed
Partners: World Bank |
In a recent call for proposals relative to the vulnerability of African Infrastructure, the World Bank expressed their interest in funding an in depth analysis including Roads, Water and Power sectors. In general terms, the objective is to detect and assess robust trans-sectoral adaptation strategies for planning, evaluating and designing specific infrastructure investments in the face of climate uncertainty.
In detail, this project focuses on the study of seven river basins in relation to four power pools applying the RAND Corporation's methods of decision under great uncertainty while using inter-related water and energy models generated by the modelling teams at SEI-US and KTH-dESA respectively, among which OSeMOSYS. The final output formulates actionable recommendations for policy makers at multiple levels on how to increase the system's resilience on the whole by enacting short term policy measures that fit into a long term vision for a robust system into the future. |
Estimating Investment Needs for the Power Sector in the Africa Region
|
Status: completed
Partner: AfDB |
Since the end of 2010, the AfDB has taken over the leadership in this area from the World Bank and has developed the Africa Infrastructure Knowledge Program (AIKP), based on the AICD methodology, as a framework for maintaining a database of infrastructure indicators. These indicators include power, water, ICT, road transport, rail transport, sea transport and air transport and are assessed for the African continent. Their responsibility also extends to generating knowledge on infrastructure on a long-term and sustainable basis.
With a focus on these responsibilities for the energy sector in particular, the approach undertaken in this project aims at updating previous assessments for selected countries while supporting the AICD view of providing a more inclusive energy dialogue. Instead of presenting one or several static sets of results, the approach invites an audience unfamiliar with modelling tools to engage in a simple form of scenario analysis. The results from numerous individual runs will subsequently be aggregated by the AfDB and made accessible through an interactive online tool for scenario description and assessment. It is expected that this will promote the understanding of basic energy system dynamics by helping the audience to perceive the influence of key parameters on energy access and hence on the evolution of energy demand and investment requirements. |